Supply Curve Shift Right
When there is an increase in demand with no change in supply the demand curve tends to shift rightwards. The supply curve will move upward from left to right which expresses the law of supply.
What Factors Change Supply Article Khan Academy
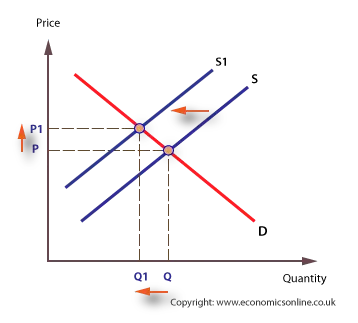
A fall in supply will mean that the curve moves leftwards.

. As the demand increases a condition of excess demand occurs at the old. These include 1 the number of sellers in a market 2. If other factors relevant.
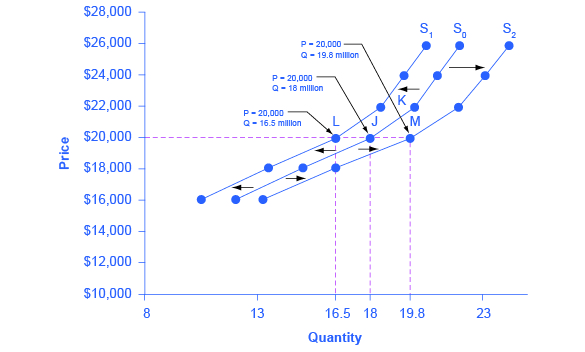
The third column decide whether the supply curve shifts to the right or left or does not shift. A supply curve shows how quantity supplied will change as the price rises and falls assuming ceteris paribusno other economically relevant factors are changing. Use Figure 1-71 to help you.
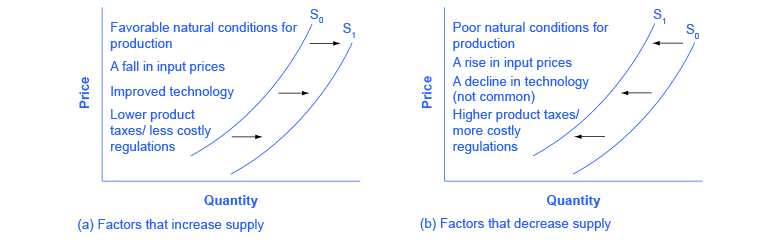
The downward shift represents the fact that supply often. A rightward shift refers to an increase in demand or supply. Increased price of factors of production.
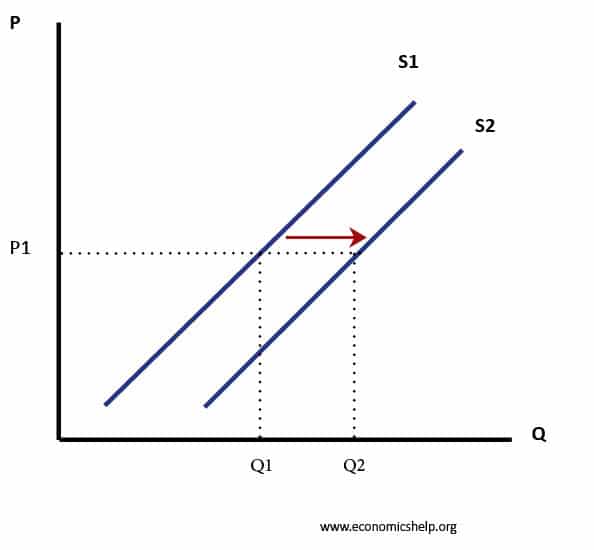
Finally indicate the letter for the new supply curve. Quantity supplied can increase as a result of a reduced cost in production of a commodity. The result is higher prices at a lower quantity.
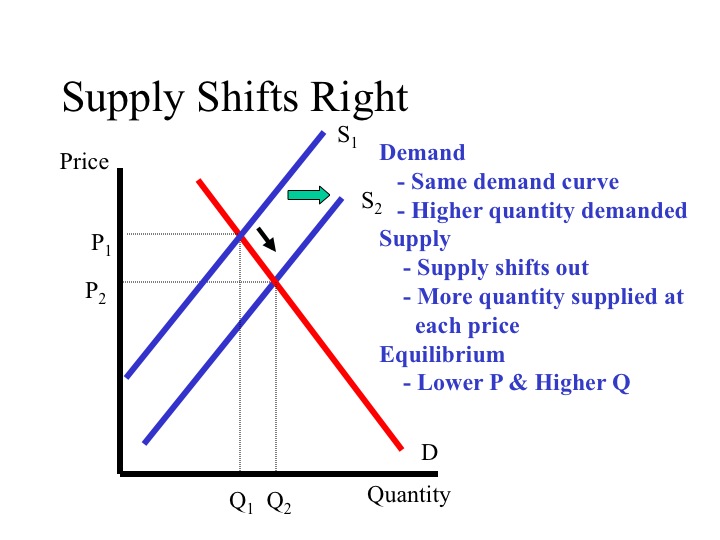
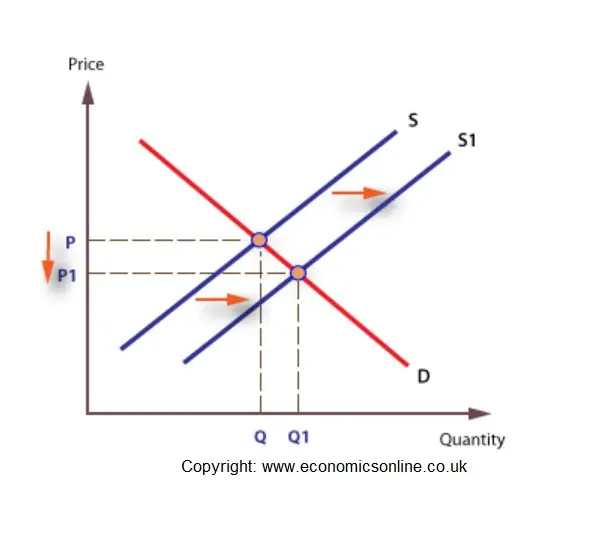
This increase will result in the downward shift of the supply curve toward the right. In this case the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts. The shift to the right shows that when supply increases producers produce and sell a larger quantity at each price.
Supply Curve Shift Right Discover free flashcards games and test prep activities designed to help you learn about Supply Curve Shift Right and other concepts. The supply curve shifts to the right because of _____. Changes in non-price factors that will cause an entire supply curve to shift increasing or decreasing market supply.
As the price of a given commodity increases the quantity supplied increases all else. If demand rises the demand curve will shift to the right. All of the above.
A reduction in the price of oil. If costs fall more can be produced and the supply curve will shift to the right. Now say that a positive supply shock occurs.
Any change in an underlying determinant of supply such as a change in the availability of factors. Each curve can shift either to the right or to the left. Thus we are in long-run equilibrium to begin.
The implication is that a larger quantity is demanded or supplied at each.
Factors Affecting Supply Economics Help
What Factors Change Supply Article Khan Academy
Comments
Post a Comment